Introduction to Gantt Charts
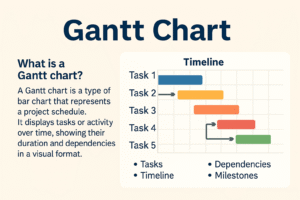
A Gantt chart is a visual project planning tool that shows tasks on a timeline. Each task is represented by a horizontal bar, making it easy to see what needs to be done, when it needs to be done, and how long it will take.
It helps teams understand the entire project at a glance — from starting date to final deadline. Because of its simplicity and clarity, Gantt charts are widely used in project management, education, business planning, construction, and even personal planning.
The main purpose is to organize work, avoid confusion, and ensure everyone stays on track.
History and Origin
The Gantt chart was developed in the early 1900s by Henry L. Gantt, an American mechanical engineer and management consultant. He introduced this chart to help factories and industries manage production schedules more efficiently.
Originally, Gantt charts were drawn manually on paper, which made updates slow and difficult. But over time, especially with the rise of computers, they evolved into dynamic digital tools used across the world.
Today, modern project management software uses Gantt charts as a core feature, making planning and tracking tasks much faster and more accurate.
Key Components of a Gantt Chart
A Gantt chart is made up of several important parts that help you understand a project’s flow:
• Tasks
These are the activities or steps that need to be completed in a project.
• Timeline
The horizontal axis showing days, weeks, or months — it represents the duration of the project.
• Bars
Each task is shown as a horizontal bar. The length of the bar indicates how long the task will take.
• Dependencies
Some tasks must be completed before others can start. These connections are shown using lines or arrows.
• Milestones
Important goals or checkpoints in the project — like major deadlines or completion of a key phase.
Together, these components help you see the ENTIRE project plan clearly and visually.
How Gantt Charts Work
A Gantt chart works by turning a project plan into a visual timeline so you can see everything at a glance.
Each task is placed on the chart as a horizontal bar, starting on the date when the task begins and ending on the date it should finish. This helps you instantly understand:
- Which tasks run at the same time
- Which tasks come first or later
- How long each task takes
- Where delays might affect overall progress
Dependencies (links between tasks) show which tasks depend on the completion of others. As each task moves forward, the chart updates to show real-time progress, making planning and tracking much easier.
In short, Gantt charts convert complex project plans into a simple, visual roadmap.
Benefits of Using Gantt Charts
Gantt charts offer several practical benefits that make project management smoother and more efficient:
• Easy Visualization
They turn complex project plans into a simple visual chart, making it easier to understand tasks and timelines.
• Improved Planning
You can plan tasks in the right order, set realistic deadlines, and avoid overlapping work.
• Enhanced Productivity
When everyone knows their responsibilities and deadlines, productivity naturally increases.
• Better Progress Tracking
You can monitor which tasks are completed, ongoing, or delayed — all in one place.
• Helps Identify Bottlenecks
If something is slowing down progress, the chart clearly highlights where the issue lies.
• Efficient Communication
Team members, managers, and clients all get a clear picture, reducing misunderstandings.
Overall, Gantt charts help teams work smarter, not harder.
Limitations of Gantt Charts
While Gantt charts are very helpful, they also have a few limitations you should be aware of:
• Can Become Complex
In large projects with hundreds of tasks, the chart can look crowded and difficult to read.
• Requires Regular Updates
If tasks change or deadlines shift, the chart needs to be updated frequently to stay accurate.
• Time-Consuming to Create
Setting up a detailed Gantt chart—especially manually—can take considerable time and effort.
• Not Ideal for Very Flexible Projects
If the project scope changes often, maintaining the chart becomes challenging.
• Can Give a False Sense of Precision
Sometimes the timeline looks perfect on the chart, but real-world delays can disrupt the plan.
Gantt charts are powerful, but they work best when managed carefully and kept up-to-date.
Types of Gantt Charts
There are mainly two types of Gantt charts based on how they are created and used:
• Traditional (Manual) Gantt Charts
These are created on paper, whiteboards, or simple tools like Excel.
They are good for small projects, but updates can be slow and time-consuming.
Best suited when the project scope is small and changes are rare.
• Digital / Software-Based Gantt Charts
These are created using project management tools or apps.
They automatically update, allow collaboration, and support dependencies, reminders, and progress tracking.
Ideal for medium to large projects where continuous changes and teamwork are involved.
Digital Gantt charts are more popular today because they are faster, accurate, and easy to manage.
Best Tools for Creating Gantt Charts
Several tools make it easy to create professional and interactive Gantt charts. Here are some of the most widely used options:
• Microsoft Project
A powerful project management software used for large and complex projects.
Offers advanced features like dependencies, resource allocation, and progress tracking.
• Microsoft Excel
A simple, accessible option.
Good for small projects where you can manually create Gantt charts using templates or conditional formatting.
• Google Sheets
Useful for collaborative teams.
Multiple people can edit the chart in real-time, making it great for remote work.
• Asana
A popular project management tool with built-in Gantt chart views (Timeline).
Helps teams plan, track, and manage tasks easily.
• Trello
Uses boards and cards, but with extensions (Power-Ups), you can add Gantt chart views.
Good for small-to-medium teams.
• Monday.com
A modern tool that offers visually appealing Gantt charts.
Useful for teams that need automation, reminders, and real-time updates.
These tools make planning more efficient, whether you’re managing a simple project or a large, multi-team workflow.
How to Create a Gantt Chart (Step-by-Step)
Creating a Gantt chart becomes very easy when you follow a simple process. Here’s how to do it:
Step 1: Identify All Project Tasks
Write down every task involved in the project.
Include big tasks, small tasks, and sub-tasks so nothing is missed.
Step 2: Define Start and End Dates
Decide when each task will begin and when it should be completed.
This helps set realistic timelines.
Step 3: Arrange Tasks in Correct Order
Some tasks must happen before others can start.
Place tasks in the right sequence to avoid confusion later.
Step 4: Add Dependencies
Mark which tasks depend on the completion of previous tasks.
This shows the flow of the project clearly.
Step 5: Assign Responsibilities
Decide who will handle each task — a team member, department, or group.
Clear ownership increases accountability.
Step 6: Draw the Timeline
Mark dates (days, weeks, or months) across the top of the chart.
Step 7: Create Bars for Each Task
Draw horizontal bars to show how long each task will take.
The start and end of each bar should match the dates you planned.
Step 8: Monitor and Update Regularly
As work progresses, update the bars to show real-time status.
This keeps the chart accurate and useful.
A well-made Gantt chart acts like a roadmap, guiding your project smoothly from start to finish.
Gantt Chart Examples
Examples make it easier to understand how a Gantt chart looks and works. Here are two common types:
• Simple Project Example
Imagine planning a school event or small assignment.
Tasks may include:
- Planning
- Budgeting
- Arranging materials
- Execution
Each task is shown as a bar on the timeline, helping you see which tasks overlap and how long each one takes.
• Business Project Example
For a business project like launching a new product, tasks may include:
- Market research
- Design
- Production
- Marketing
- Final launch
A Gantt chart shows all these activities in order, their duration, dependencies, and deadlines.
This helps managers track progress easily and avoid delays.
These examples show how Gantt charts bring clarity, structure, and coordination to any type of project — small or big.
Applications of Gantt Charts
Gantt charts are used in many fields because they make planning, tracking, and organizing work much easier. Here are the most common areas where they are widely used:
• Business Projects
Companies use Gantt charts to plan product launches, marketing campaigns, sales strategies, and operational tasks.
They help teams stay aligned and meet deadlines.
• Construction
Construction projects have many stages like planning, design, material purchase, and building work.
A Gantt chart helps coordinate all these steps and ensure the project stays on schedule.
• Education
Teachers, students, and schools use Gantt charts to plan assignments, exams, events, and long-term projects.
They make academic planning more systematic.
• Event Management
Events like conferences, cultural programs, and weddings need proper scheduling.
A Gantt chart helps organize tasks such as booking, logistics, invitations, and rehearsals.
• Software Development
Developers use Gantt charts to manage coding tasks, testing phases, updates, and release cycles.
It ensures the team works efficiently and meets project milestones.
• Healthcare & Administration
Hospitals and administrative teams use Gantt charts for planning staff schedules, health camps, training sessions, and facility upgrades.
Overall, Gantt charts are practical tools used across almost every industry because they improve clarity, coordination, and control over projects.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While using Gantt charts, people often make some mistakes that can affect project planning. Avoiding these helps keep your chart accurate and useful.
• Adding Too Many Tasks
Overloading the chart with unnecessary details makes it confusing.
Focus only on important tasks and milestones.
• Not Updating the Chart Regularly
If tasks change or get delayed, the chart must be updated.
An outdated chart leads to poor decisions.
• Ignoring Dependencies
Skipping task dependencies can create unrealistic timelines.
Dependencies show the real flow of the project.
• Setting Unrealistic Deadlines
If deadlines are too tight, the team becomes stressed and the plan fails.
Create timelines based on actual effort.
• Not Assigning Ownership
If tasks are not assigned properly, accountability decreases.
Everyone should know their role.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you make your Gantt chart more effective, practical, and reliable.
Tips for Using Gantt Charts Effectively
To get the best results from a Gantt chart, a few smart practices can make a big difference:
• Keep the Chart Simple
Avoid overcrowding it with extra details.
A clean, easy-to-read chart improves understanding.
• Update Regularly
As tasks progress or change, update the chart so it always reflects the current status.
• Use Color Coding
Different colors for teams, task types, or priorities make the chart more readable and visually organized.
• Break Down Big Tasks
Large tasks can be split into smaller sub-tasks for better clarity and tracking.
• Review with the Team
Discuss the chart regularly in team meetings.
This keeps everyone aligned and reduces confusion.
• Use the Right Tool
Choose software that fits your project size — simple tools for small projects and advanced tools for complex ones.
Using these tips helps make your Gantt chart more practical, easy to manage, and highly effective for any project.
Conclusion
Gantt charts are one of the most effective tools for planning, organizing, and tracking projects. They turn complex project details into a simple visual timeline that helps teams understand what needs to be done and when.
With clear tasks, timelines, dependencies, and progress updates, Gantt charts make it easier to:
- Stay organized
- Manage time effectively
- Improve teamwork
- Predict delays early
- Complete projects on schedule
Whether it’s a small school project or a large business operation, a well-designed Gantt chart provides structure, clarity, and confidence.
In simple words, a Gantt chart is a roadmap that guides a project from start to finish.